PTBD in biliary obstruction
Biliary obstruction commonly refers to blockage of the bile duct system leading to impaired bile flow from the liver into the intestinal tract. Bile is a substance that contains bile salts, bilirubin, and cholesterol and is continuously synthesized in the liver hepatocytes.
What are the symptoms of biliary obstruction?
Symptoms
- Abdominal pain in the upper right side.
- Dark urine.
- fever
- itching
- Jaundice (yellow skin color)
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Clay-colored or pale stools.
Causes
Bile is a liquid released by the liver.
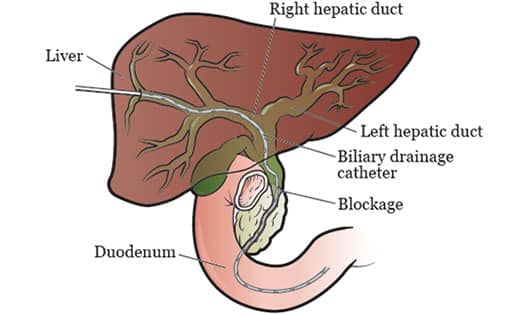
When the bile ducts become blocked, bile builds up in the liver, and jaundice (yellow color of the skin) develops due to the increasing level of bilirubin in the blood.
The possible causes of a blocked bile duct include:
- Cysts of the common bile duct
- Enlarged lymph nodes in the porta hepatis
- Gallstones
- Inflammation of the bile ducts
- Narrowing of the bile ducts from scarring
- Injury from gallbladder surgery
- Tumors of the bile ducts or pancreas
- Tumors that have spread to the biliary system
- Liver and bile duct worms (flukes)
The risk factors for a blocked bile duct include:
- History of gallstones, chronic pancreatitis, or pancreatic cancer
- Injury to the abdominal area
- Recent biliary surgery
- Recent biliary cancer (such as bile duct cancer)
The blockage can also be caused by infections. This is more common in people with weakened immune systems.
Exams and Tests
The following blood test results could be due to a possible blockage:
- Increased bilirubin level
- Increased alkaline phosphatase level
- Increased GGT enzyme level
- Increased liver enzymes
The following tests may be used to investigate a possible blocked bile duct:
- Abdominal ultrasound
- Abdominal CT scan
- Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP)
- Percutaneous transhepatic cholangiogram(PTCA)
- Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP)
- Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS)
A blocked bile duct may also alter the results of the following tests:
- Amylase blood test
- Gallbladder radionuclide scan
- Lipase blood test
- Prothrombin time (PT)
- Urine bilirubin
Treatment
The goal of treatment is to relieve the blockage. using an endoscope during an ERCP.
In some cases, surgery is required to bypass the blockage
If the blockage is caused by cancer, the duct may need to be widened. This procedure is called percutaneous (through the skin next to the liver) dilation. A tube may need to be placed to allow drainage.
PTBD:
If the blockage is caused by cancer, the duct may need to be widened. This procedure is called percutaneous (through the skin next to the liver) dilation. A tube may need to be placed to allow drainage.
Book An Appointment
Outlook (Prognosis)
If the blockage is not corrected, it can lead to life-threatening infection and a dangerous buildup of bilirubin.
If the blockage lasts a long time, chronic liver disease can result. Most obstructions can be treated with endoscopy or surgery. Obstructions caused by cancer often have a worse outcome.
Possible Complications
Left untreated, the possible complications include infections, sepsis, and liver disease, such as biliary cirrhosis.7
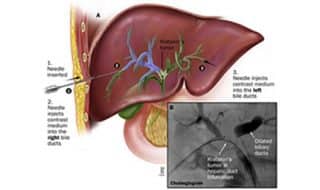
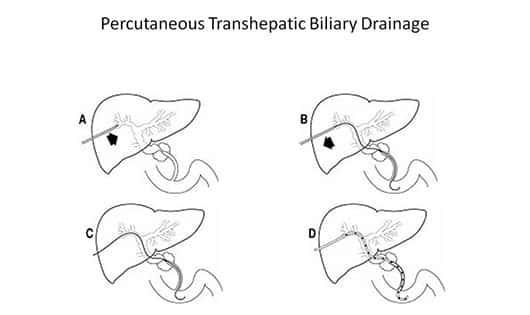
PTBD (PERCUTANEOUS TRANSHEPATIC BILIARY DRAINAGE)
What is PTBD?
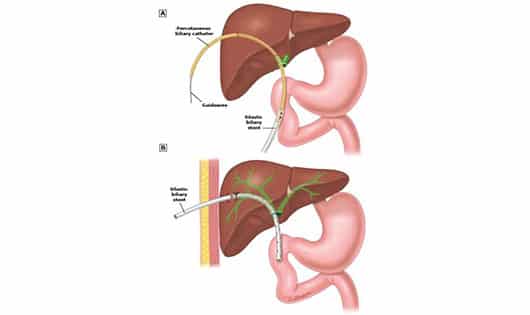
Procedure in which the bile duct punctured through skin and liver by a needle under ultrasound guidance. Wire is placed followed by catheter. This procedure is done under local anesthesia or mild sedation. It is bassically to direct the accumulated / obstructed bile in the liver either exterally or to direct the bile via a tube negociated across the narrowed part of the biliary duct into duodenum. Thus relieves the bile load on the liver.
Biliary externalization: In cases where wire can’t go beyond obstruction or patients with active infection
Biliary internalization: Bile is to be drained within only; no external bag. For malignancy metallic stent is placed.
ADVANTAGE:
When ERCP fails or when the pt is not a fit candidate for ERCP/ anesthesia or when the anatomy post surgery is complicated, PTBD can be easily done.
- No general anesthesia
- Day care procedure
- High success rate
- Non surgical.