Stenting By India's Premier Vascular Surgeons
We, Vascular Interventions have the Endovascular Surgeon in Hyderabad gives the treatment by following the best procedures, which provide minimally invasive treatment for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm. An Aortic Aneurysm is a fragile area in the aorta, the main blood vessel that carries blood from the heart to the rest of the body. As blood flows through the arterial blood vessel, the weak space bulges sort of a balloon and might burst if the balloon gets too huge.
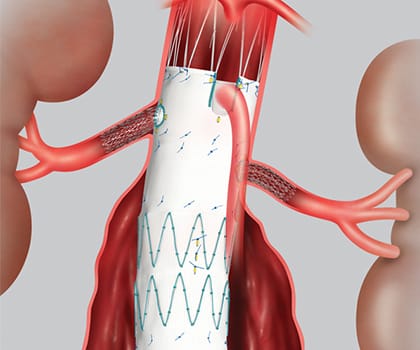
Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm is a weakened space within the main vessel that Supplies blood from the Heart to the other parts in the body. Once blood flows through the arterial blood vessel, the pressure of the blood beats against the weakened wall, which then bulges sort of a balloon. If the balloon grows giant enough, there’s a danger that it’ll burst. Most typically, aortal aneurysms occur within the portion of the vessel below the artery origins. The aneurysm might extend into the vessels provision the hips and pelvis. Once an abdominal aneurysm reaches 5cms in diameter, it’s sometimes looked-for to treat to stop rupture. Below five centimeters, the chance of the aneurysm rupturing is less than the chance of standard surgery in patients with traditional surgical risks. The goal of medical care for aneurysms is to stop them from rupturing. Once abdominal aorta aneurysm has damaged, the probabilities of survival area unit are low, with 80-90 % of all damaged aneurysms leading to death. These deaths are often avoided if an aneurysm is detected and treated before it ruptures.
AAA is often called a “silent killer” because there are usually no noticeable symptoms of the disease. Three out of four aneurysms show no symptoms at the time they’re diagnosed. When symptoms are present, they may include:
- Abdominal pain (that could also be constant or come and go)
- Pain in the lower back that may radiate to the buttocks, groin or legs
- The feeling of a “heartbeat” or pulse within the abdomen
- Once the aneurysm bursts, symptoms include:
- Severe back or abdominal pain that begins suddenly
- Paleness
- Dry mouth/skin and excessive thirst
- Nausea and vomiting
- Signs of shock, such as shaking, dizziness, fainting, sweating, and rapid heartbeat.
At present there are 3 treatment options for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm:
Watchful Waiting
Little AAAs (less than 5 cms or about 2 inches), that don’t seem to be rapidly growing or inflicting symptoms, have a low occurrence of rupture and sometimes require no treatment apart from watchful waiting under the guidance of an Endovascular Surgeon in Hyderabad. This typically includes follow-up ultrasound exams at regular intervals to determine if the aneurysm has developed.
Surgical Repair
The foremost common treatment for an outsized, un-ruptured aneurysm is open surgical repair by a vascular surgeon. This procedure involves an incision from the slightest below of the breastbone to the highest of the pubic bone. The Endovascular Surgeon in Hyderabad then clamps off the aorta, cuts open the aneurysm and sews in a graft to act as a bridge for the blood flow. The blood flow then goes through the plastic graft and no longer allows the direct pulsation pressure of the blood to further expand the frail aorta wall.
Interventional Repair
Interventional Radiologists perform the minimally invasive technique using imaging to guide the catheter and graft within the patient’s artery. For this procedure, an incision is made in the skin at the groin where the catheter is passed into the femoral artery and then directed to the aortic aneurysm. Now, the physician passes a stent graft that is compressed into a small diameter through the catheter. The stent-graft is advanced to the aneurysm and then opened, creating new walls in the blood vessel where the blood flows. This less invasive technique of inserting a graft within the aneurysm to redirect blood flow and stop direct pressure from being exerted on the weak aortic wall. This comparatively new technique eliminates the necessity for an outsized abdominal incision. It conjointly eliminates the necessity to clamp the aorta throughout the procedure. Clamping the aorta creates major stress on the heart, and people with severe heart disease may not be able to tolerate this major surgery. Stent grafts procedure is most commonly considered for patients at increased surgical risk due to age or other medical conditions; but not for everyone. It is still a new technology and we don’t yet have data to show that this will be a sturdy repair for long years. Thus, people with a life span of 20 or more years may be counseled against this therapy. It is also a technology that’s restricted by size, as the grafts aren’t custom-built for each patient’s anatomy.
Depends on the treatment given.
Q: What size aortic aneurysm is dangerous?
A: The need for surgical treatment is related to size, which is linked to the risk of rupture. Elective repair should be considered for aneurysms > 5.0 to 5.5 cm.
